Die Cutting Companies
Die cutting is the manufacturing process of stamping or cutting two dimensional parts out of flat sheets of materials like rubber, fiber, paper, or metals. This process, often used in conjunction with laminating services, is a crucial finishing service for a wide range of parts and products.
We know that high tech products require die cut parts that are created with precision and care. We have the highest quality standards in the die cutting industry because we know that with die cutting accuracy is so important. After we cut the prototype for your product and after receiving your approval we pledge that your orders will be shipped within ten business days or less.
CFS provides laser die cut services. Finished product can be supplied as individual pieces or on rolls. As a standalone service, the laser can create nearly perfect parts with tolerances as close as +/-0.002". Unlike traditional die cutting methods, the laser can create tricky patterns and fine details which are otherwise impossible. Offering advanced optical registration and vision inspection...
When it comes to die cutting, we are the experts! We are a Grand Rapids, Michigan based company but we offer our services to all across the United States. It is our goal to bring exceptional die cutting services to all of our clients while also providing customer service that will keep you coming back to fulfill all of your die cutting needs. Our staff has the experience you can count on to...
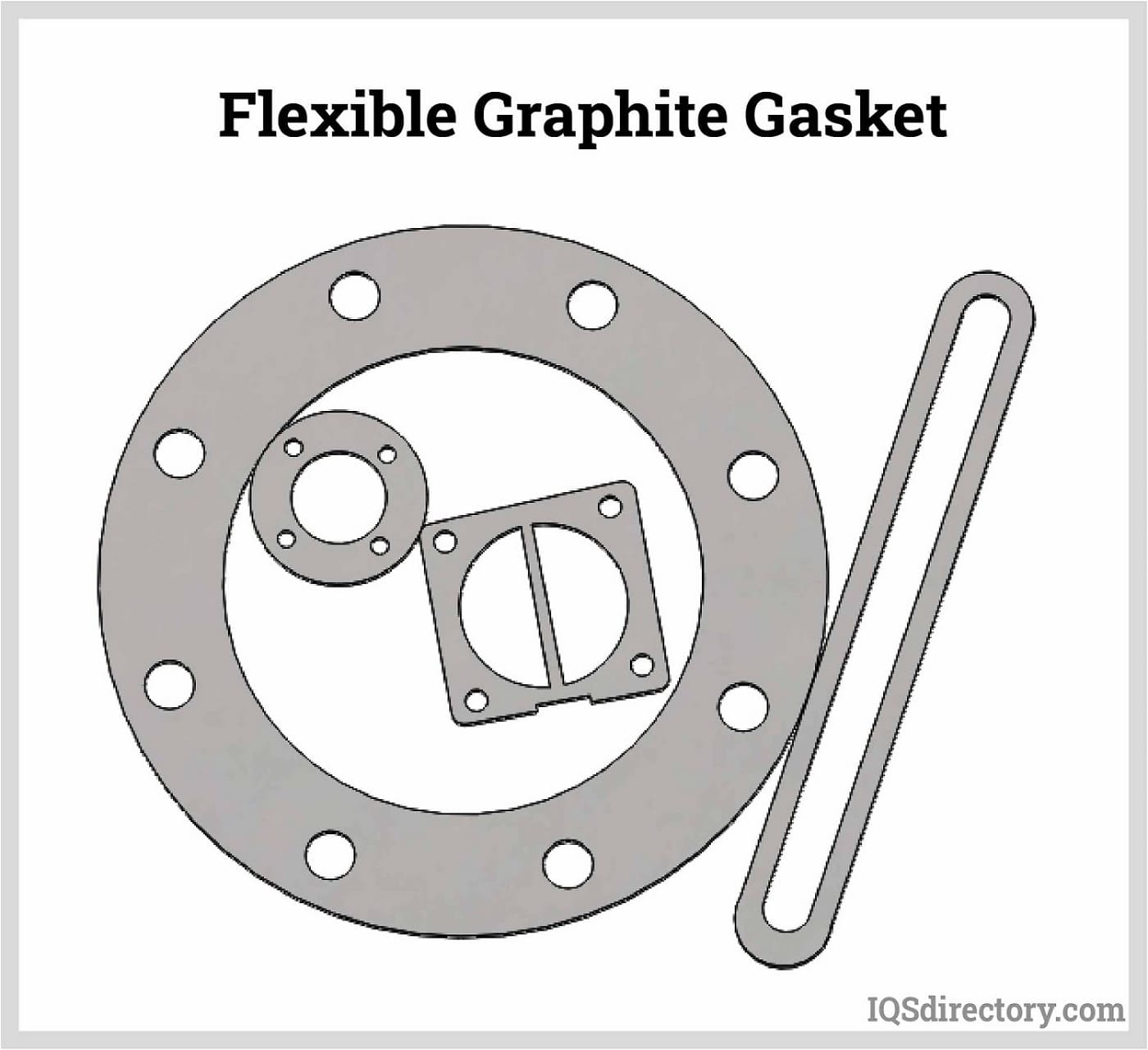
Gardico has been providing superior products and workmanship to industrial customers since 1977. Our die cutting capabilities satisfy needs for standard and custom gaskets, pads, insulators and decorative pieces in quantities from 5 or 10 to tens of thousands.

REDCO offers complete die cutting services to produce custom die cut gaskets and other custom die cuts that perfectly match our customers’ specifications. All of our steel rule dies are laser cut to guarantee quality and accuracy of the finished product. We have over 70 years of experience in die cutting non-metallic and metal parts. We strive to provide the best possible prices, the...
More Die Cutting Companies
Die cutting stamps or cuts two-dimensional parts from flat sheets of materials like rubber, fiber, paper, or metals. Often paired with laminating services, it provides a crucial finishing touch for various parts and products. Although the term “die cutting” can be ambiguous and varies across fields, it generally involves more than just cutting. Dies also form shapes by using compression and other stress methods to achieve desired shapes.
Die Cutting Process
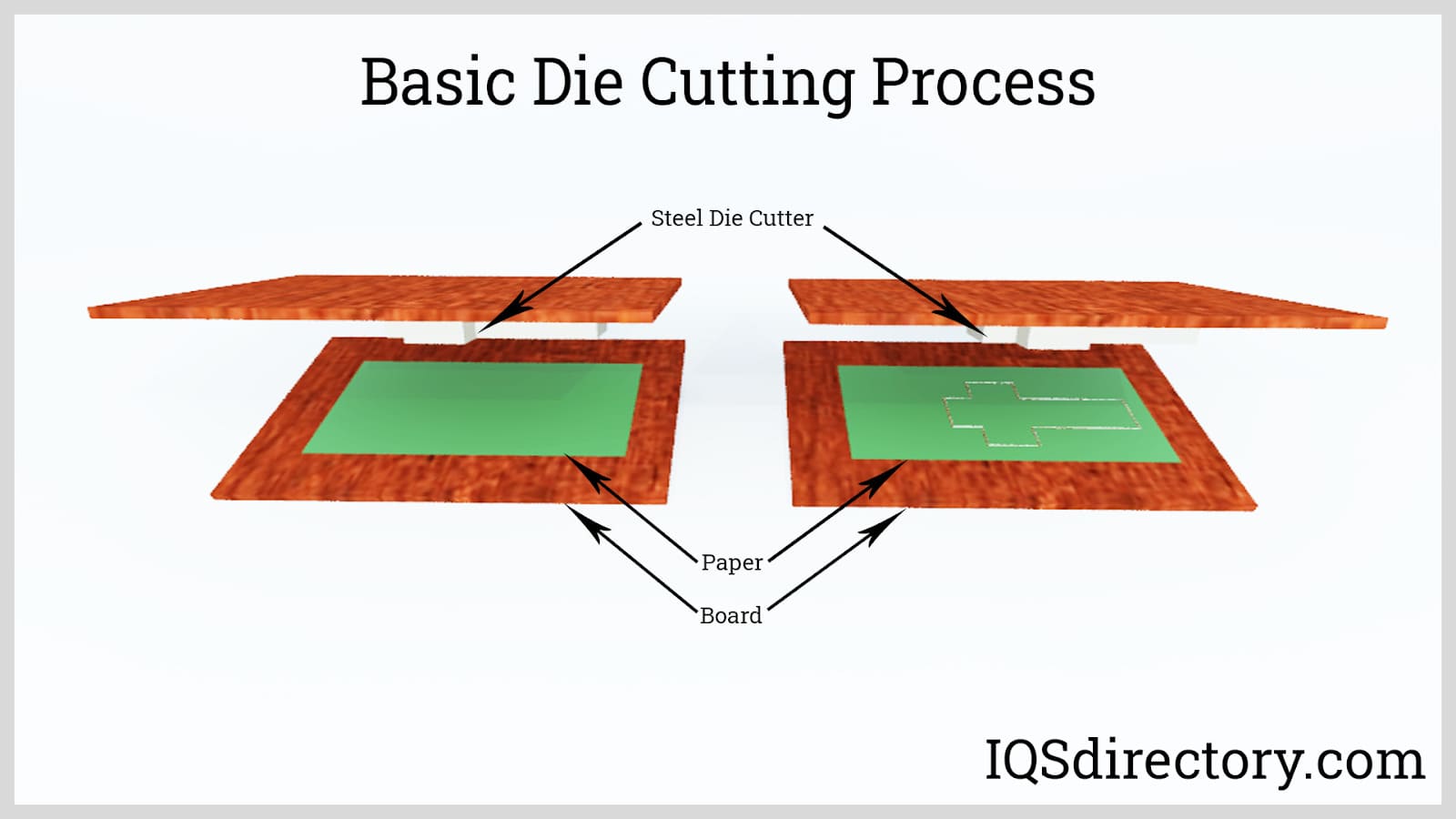
Die cutting is a precise and versatile process essential for creating uniform shapes from various materials. It starts with designing the desired shape, which is then made into a die—a tool typically crafted from durable steel. The die, featuring sharp blades or edges, cuts through the chosen material to produce the required shape.
Once the die is prepared, the material—whether paper, fabric, plastic, rubber, foam, or thin metal sheets—is readied for processing. It is usually on large spools or in sheets, ready for the die cutting machine. As the material moves through the machine, it contacts the precisely positioned die. The machine applies pressure, and the die’s sharp blades cut the material into the desired shape, ensuring clean, accurate cuts and uniform shapes that meet strict specifications.
After die cutting, the finished shapes are separated from the leftover material, known as the “web” or “skeleton.” This waste is removed, leaving the final die-cut products. The process is highly efficient, enabling the production of many identical shapes quickly.
Quality control is crucial in die cutting. Inspections ensure the products meet required standards and match the intended design. Any defective pieces are identified and removed, minimizing waste and maintaining high quality.
Additional processes often follow die cutting, tailored to the specific application and product requirements. In the packaging industry, die-cut boxes typically undergo folding and gluing to form the final structure. In textiles, die-cut fabrics move on to sewing and assembly to create finished garments or accessories.
Types of Die Cutting
The die cutting process varies, employing different equipment based on specific applications and materials. It can be categorized into several methods, each designed to meet distinct production requirements.
Flatbed Die Cutting
Flatbed die cutting stands as the most common method in the die cutting industry. Utilizing a flatbed press, this technique effectively stamps out shapes from flat materials with precision and efficiency. It is particularly favored for its versatility and reliability in handling a variety of materials, including paper, cardboard, and certain types of plastics.
This method excels in producing a diverse array of products, such as labels, business cards, and packaging materials. The flatbed press ensures clean, accurate cuts, making it an ideal choice for applications that demand high-quality finishes. Its widespread use across various industries highlights its importance in manufacturing processes that require detailed and consistent outcomes.
Rotary Die Cutting
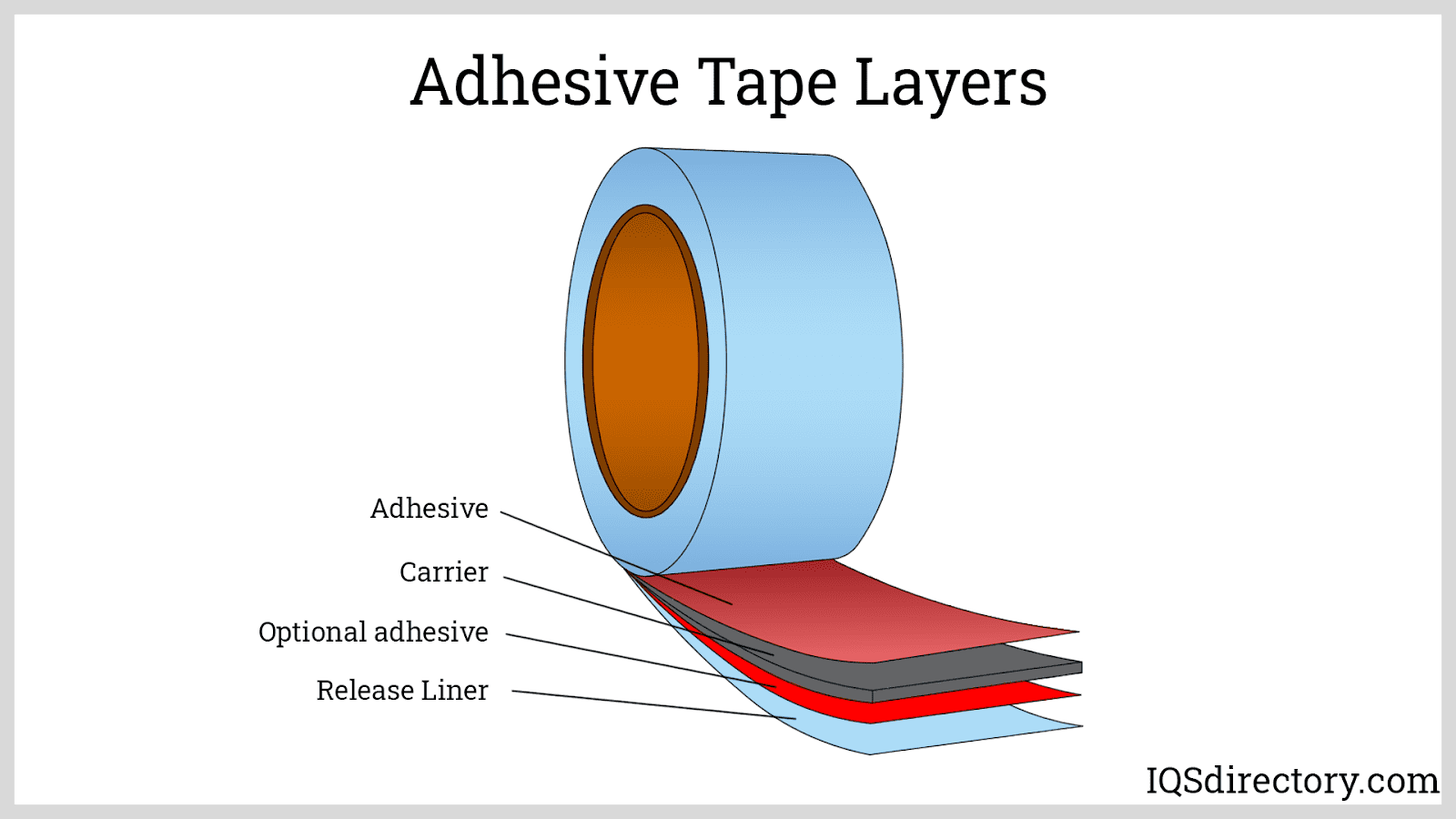
Rotary die cutting utilizes a cylindrical die to precisely cut materials presented in a continuous roll or web format. This method is exceptionally efficient, making it ideal for the high-volume production of items such as labels, tapes, and adhesive-backed products. By processing materials on rolls, rotary die cutting significantly reduces the need for frequent reloading, thereby enhancing production speed and efficiency. This technique is particularly advantageous in industries where large quantities of uniformly cut materials are required, ensuring consistent quality and optimal use of resources.
Steel Rule Die Cutting
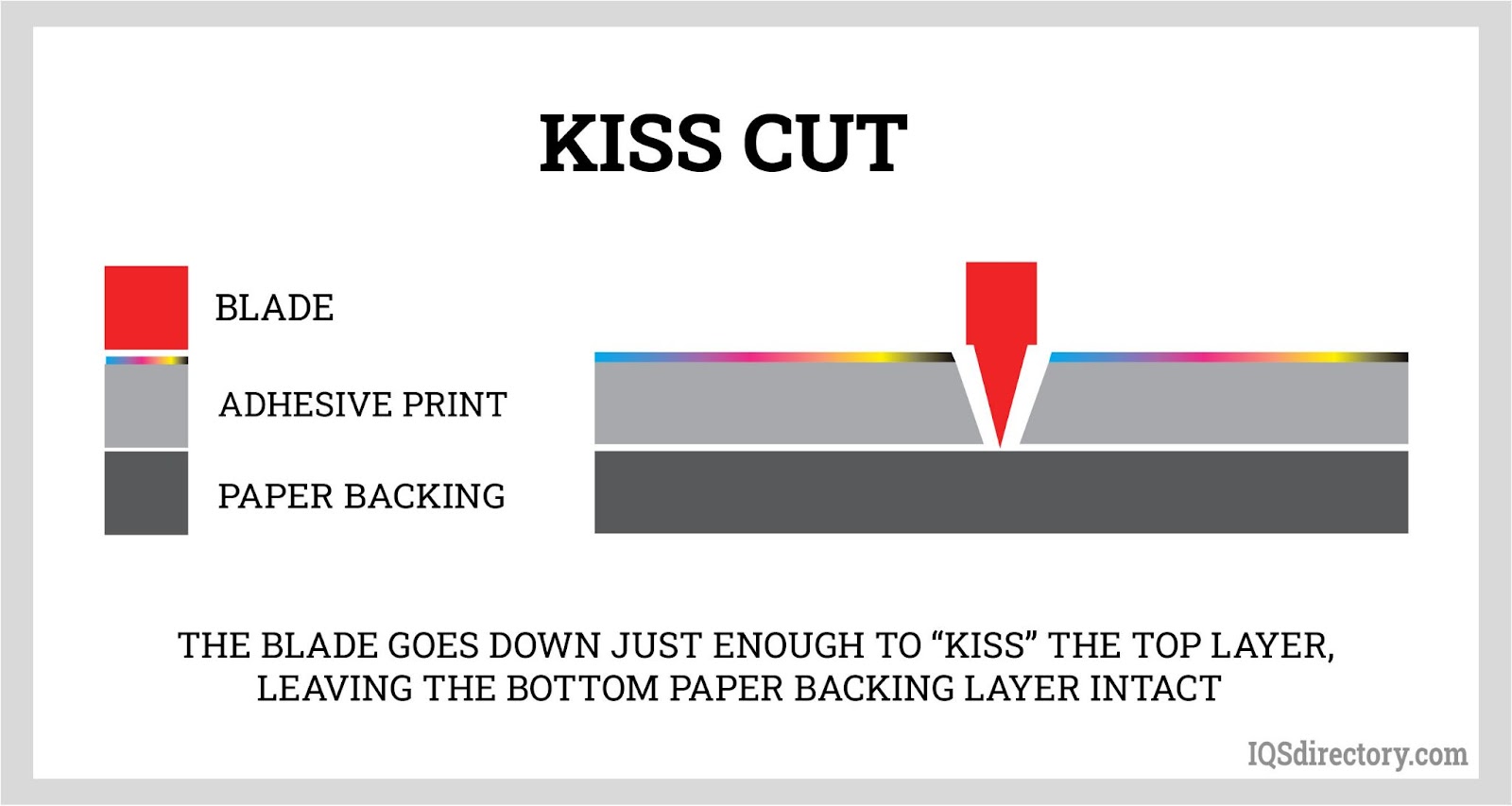
Steel rule die cutting is a process where sharp blades are embedded into a wooden or acrylic base to create a flexible die. This type of die is particularly effective for cutting soft and compressible materials like foam, gaskets, and specific fabrics. The technique offers precision and versatility, making it an ideal choice for industries that require accurate and consistent cutting.
Laser Die Cutting
Laser die cutting employs lasers to cut materials with high precision, unlike traditional physical dies. This method excels in producing intricate and complex designs, offering significant flexibility for design changes without requiring new physical dies. It is particularly effective for materials such as plastics, rubber, and thin metal sheets, providing a versatile and efficient solution for various industries.
Waterjet Die Cutting
Waterjet Die Cutting is a highly effective technique that utilizes high-pressure waterjets, often enhanced with abrasive substances, to precisely cut through a wide range of materials. This method is particularly advantageous for cutting materials that could be compromised by conventional cutting techniques, such as heat-sensitive foams or rubber. By employing waterjet die cutting, manufacturers can achieve clean, precise cuts without the risk of damaging the material’s integrity. This makes it an ideal solution for industries requiring meticulous and damage-free cutting processes.
Choose die cutting methods and equipment based on material type, thickness, design complexity, production volume, and precision requirements. Sometimes, combining different die cutting methods achieves the best results. Manufacturers and industries can optimize production efficiency, reduce material waste, and ensure consistent high-quality output by selecting the most suitable die cutting approach.
History of Die Cutting
Die cutting began in the mid-1800s in the shoe industry, replacing the labor-intensive process of hand-punching holes in leather. This innovation sped up leather cutting, allowing shoemakers to easily shape leather using a press fitted with a cut die.
In the early 1900s, die cutting technology advanced with the invention of the swing arm clicker press. This tool enabled users to cut various shapes and sizes simultaneously using different dies, paving the way for mass production of products like plastic and metal tubing.
In the 1950s, engineers started developing increasingly smaller machine models, including handheld and tabletop versions. Since the early 2000s, die cutting has been transformed by computers and CAD technology. Modern die cutting processes now incorporate advanced robotics and high-pressure presses capable of cutting through even the thickest hard metals.
Today, die cutting machines are not only used for commercial and industrial applications but are also available for crafting at home or in classrooms. A notable example is the Cricut Expression, a small, portable die cutting machine that can be programmed with various fonts and shapes available through physical or digital Cricut cartridges.
Limitations of Die Cutting
Die cutting excels in producing simple to moderately complex shapes, but it struggles with intricate and highly detailed designs, especially in thicker or harder materials. Although laser die cutting offers more flexibility for complex designs, it isn’t suitable for all materials or production volumes. Die cutting performs best with flat, uniformly thick materials; thick or rigid materials can stress the equipment, and delicate or brittle materials may suffer damage during the cutting process. Additionally, the setup and tooling costs for die cutting can be significant, particularly for custom shapes or small production runs, making it less economical for short or one-time jobs.
The die cutting process generates waste material known as the “web” or “skeleton,” leading to material wastage. To minimize waste and maximize efficiency, manufacturers must optimize the die layout. Precise alignment between the die and material is crucial to maintain quality and consistency; misalignment can cause defects that impact the product’s appearance and functionality. Die cutting is also limited by material thickness; beyond a certain point, the required pressure becomes impractical, necessitating alternative methods like machining or waterjet cutting.
Advancements of Die Cutting
Manufacturers have embraced advanced technology and automation to enhance die cutting. By using CAD software and automated die cutting machines, they achieve precise and consistent intricate designs. CAD allows for detailed, customized dies, while automation ensures accurate alignment, reducing defects.
For cutting thicker or tougher materials, manufacturers use multi-step die cutting. This involves multiple passes, gradually increasing pressure and depth, enabling precise processing while minimizing damage to the die and material.
To address material waste, manufacturers optimize die layouts using nesting algorithms. These algorithms arrange shapes on the material to maximize usage and minimize waste, enhancing material efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Innovative manufacturers also explore hybrid cutting methods. By combining die cutting with technologies like laser or waterjet cutting, they expand the range of materials and designs that can be processed. Hybrid techniques allow for handling challenging materials and designs that traditional die cutting alone cannot manage effectively.
Benefits of Die Cutting
Die cutting provides numerous benefits that make it invaluable across various industries. First, it ensures precision and uniformity in shapes and dimensions. Specialized dies facilitate consistent cutting, resulting in identical products with minimal variation. This accuracy is particularly crucial in industries such as electronics and automotive, where precise components are essential for proper functionality and assembly. Second, die cutting enables the creation of intricate and complex designs. Whether producing delicate patterns for paper crafts or precise gaskets for industrial applications, die cutting allows for detailed shapes that might be challenging or time-consuming to achieve through other methods.
Third, die cut items typically feature smooth and clean edges, enhancing both their appearance and usability. This is particularly important in industries like packaging and textiles, where neat finishes are vital for aesthetic appeal and user experience. Furthermore, die cutting is a cost-effective solution for high-volume production. Once the dies are created, the production process becomes highly efficient, reducing labor costs and increasing output.
Die cutting offers several distinct advantages compared to other similar procedures. Primarily, it is renowned for its high-speed production capabilities, efficiently producing large volumes of identical items quickly, which is ideal for mass production. In contrast, manual cutting and some laser cutting techniques are more time-consuming and labor-intensive. Additionally, die cutting is highly versatile, accommodating a wide range of materials such as paper, fabric, plastics, rubber, foam, and thin metal sheets, making it useful across various industries. Other cutting methods may be restricted to specific materials, limiting their applications. Lastly, die cutting ensures consistent and repeatable results. Once the dies are set up, they deliver high accuracy and precision, minimizing defects and waste. Other cutting methods might have higher tolerances, resulting in variable outcomes and necessitating additional quality checks.
Die cutting offers the advantage of efficiently producing complex shapes. Unlike laser cutting, which can be time-consuming for intricate designs, die cutting performs quickly and precisely. This makes it ideal for crafting, product packaging, and custom components. Additionally, die cutting is cost-effective, especially for high-volume production, as the process becomes highly automated once the dies are created, reducing labor costs and increasing production rates. Other methods, such as waterjet or manual cutting, are more labor-intensive and costly. Overall, die cutting is a popular and efficient choice in many manufacturing applications due to its speed, precision, and cost benefits.
Applications of Die Cutting
Die cutting is a versatile manufacturing process widely used across various industries. Some of the industries that make use of die cutting technology include printing, packaging, textiles, automotive, electronics, medical, furniture, manufacturing, aerospace, and military sectors.
Die cutting is a pivotal process in the printing and packaging sector, transforming flat materials into precisely shaped items such as business cards, brochures, folders, labels, and packaging boxes. This technique ensures uniformity and boosts visual appeal. Additionally, die cutting enables the creation of bespoke packaging designs, tailored to fit specific product requirements, making it an indispensable element in effective branding and marketing strategies. Within the textiles and apparel industry, die cutting is utilized to cut fabric into specific shapes for garments, accessories, and home furnishings. From detailed appliques to custom patches, this method guarantees precision and consistency, streamlining the assembly process and enhancing the quality of the final products.
Die cutting plays a crucial role in the automotive industry, producing gaskets, seals, and interior components. It ensures precise fits for gaskets, enabling efficient engine and system operation. Additionally, die-cut interior parts like foam inserts and padding enhance vehicle comfort and safety. In the electronics sector, die cutting creates essential components such as insulators, shields, and adhesive pads. These parts are vital for the proper functioning and protection of electronic devices. For example, die-cut adhesive pads simplify the assembly and bonding of components during manufacturing.
Die cutting is widely used in the medical sector for crafting items such as wound dressings, medical device parts, and diagnostic test strips. The meticulous nature of die cutting guarantees that medical products adhere to strict quality standards, delivering dependable performance and precision. Die cutting is a favorite in the stationery and crafting worlds for making elaborate designs and shapes. Items like greeting cards, invitations, stickers, and scrapbooking elements are frequently produced using die cutting. The capacity to generate distinctive and detailed designs makes die cutting a preferred method for crafters and DIY enthusiasts.
Die cutting plays a pivotal role in various industries, crafting custom components like gaskets, seals, and insulators that ensure the efficient and safe operation of machinery and equipment. In the aerospace and defense sectors, this technique is essential for producing specialized parts such as thermal and acoustic insulation materials, gaskets, and sealing solutions, which are vital for the safety and performance of aircraft and defense systems. Renowned for its precision, efficiency, and versatility, die cutting has become an indispensable part of modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of consistent, custom-shaped items that enhance the quality and functionality of products across diverse applications.
Choosing the Right Die Cut Manufacturer
For the best results when choosing a die cut manufacturer, use our directory to compare multiple companies. Each manufacturer has a detailed profile showcasing their expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form for inquiries or quotes. Our patented website previewer lets you quickly understand each company’s specialties. Finally, use our streamlined RFQ form to contact multiple manufacturers simultaneously.
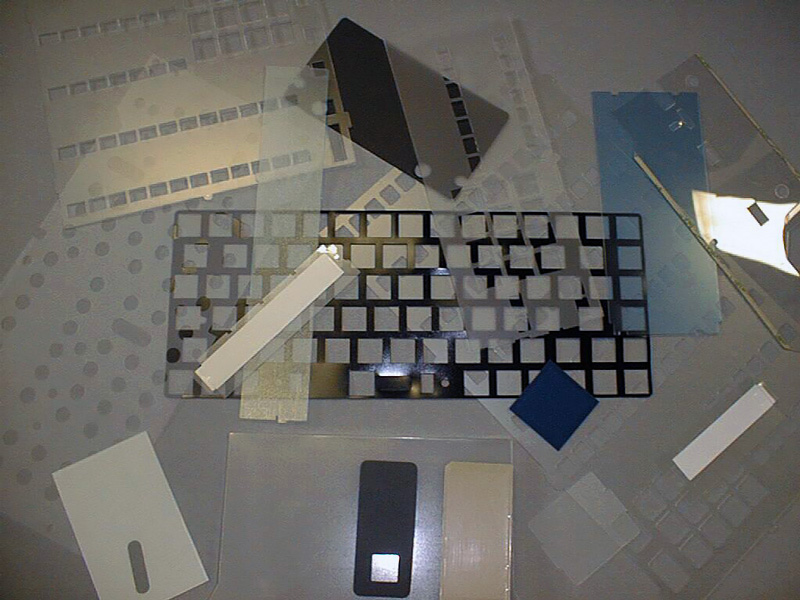


 Die Cutting
Die Cutting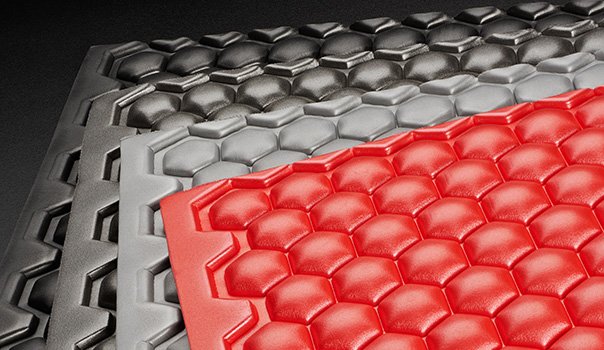 Foam Fab
Foam Fab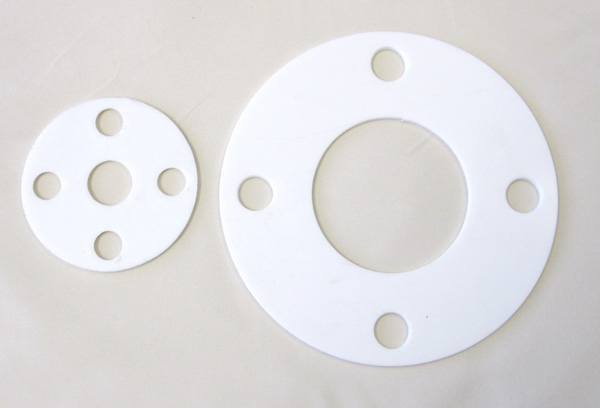 Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services